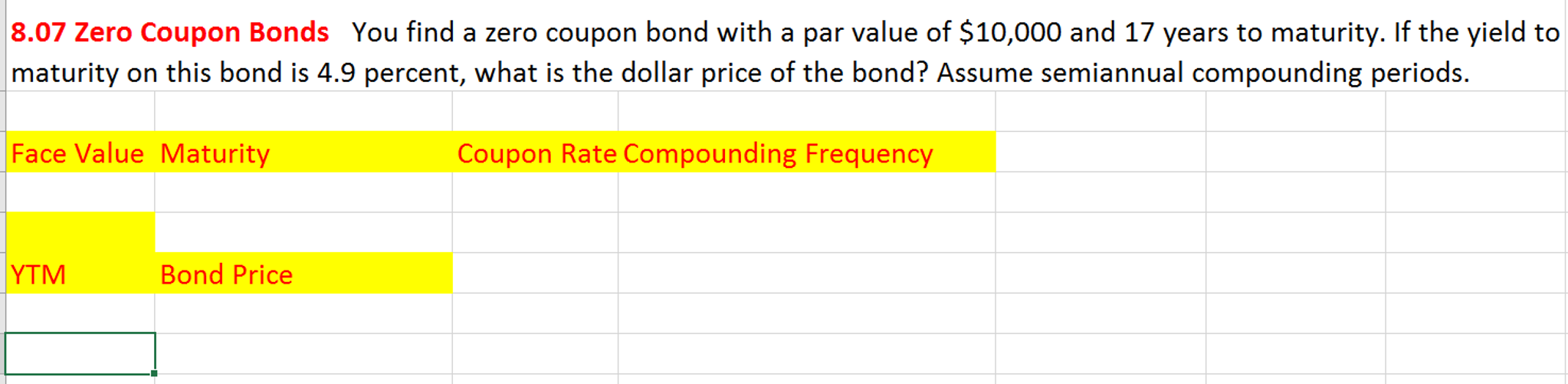
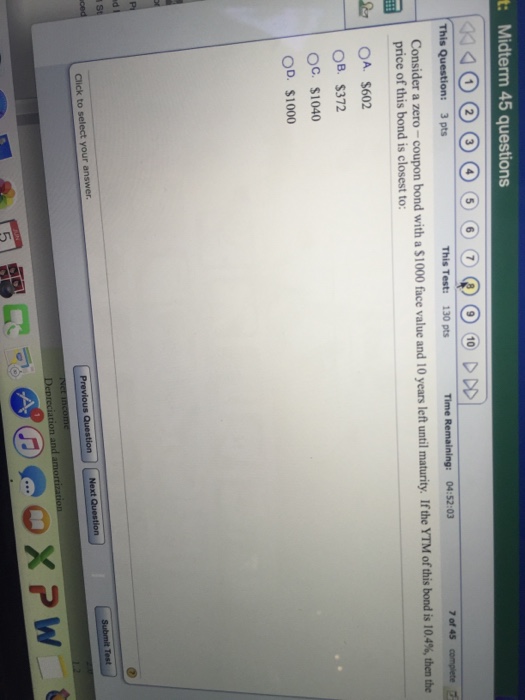
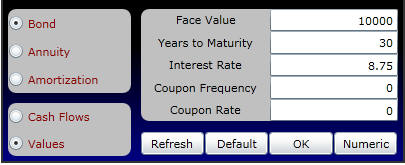
38 zero coupon bond journal entry
Bonds Payable | Journal Entries | Examples - XPLAIND.com Example: Journal Entries. On 1 January 2001, Codestreet, Inc. issued 100,000, $100 face value bonds carrying a coupon rate of 8% payable semiannually. The term of the bonds is 20 years. Journalize issuance of bonds and the first semi-annual payment. Solution. Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia A zero-coupon bond is a debt security instrument that does not pay interest. Zero-coupon bonds trade at deep discounts, offering full face value (par) profits at maturity. The difference between...
14.4 Pricing and Reporting Term Bonds - Financial Accounting Prepare all journal entries for a term bond when the stated cash interest rate is different from the effective interest rate. Question: Although zero-coupon bonds are popular, notes and most bonds actually do pay a stated rate of cash interest, one that is specified in the contract. ... Earlier, with the zero-coupon bond, the entire amount of ...

Zero coupon bond journal entry
Fountain Essays - Your grades could look better! Journal article. Social Relations. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Psychology. 2. View this sample Project. Research. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Political science . 3. View this sample Response essay. ntroduction to Embedded Software Verification Comparison of Model Checking Tools for Information Sys. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Computer science. 2. View this sample Reflection paper/Reflection essay. Writer's choice ... Accounting for Issuance of Bonds (Example and Journal Entry) Suppose ABC company issues a bond at a par value of $ 100,000 and a coupon rate of 5% with 5 years maturity. The market interest rate is also 5%. Let us calculate the PV of bond principal payment and interest component first. PV of bond = $ 100,000 × (0.78355) = $ 78,355. PV Factor 5%, 5 years = 0.78355. Coupon/Interest = $ 100,000 × 5% ... PubMed Moved Permanently. The document has moved here.
Zero coupon bond journal entry. Answered: Assume a firm issues a zero-coupon bond… | bartleby Make the journal entry to issue the bonds on 1/1/2021 iii. Make the entry to record interest on 12/31/2021 and 12/31/2022. iv. Make the entry to retire the principle of the bonds on 12/31/2040v. For every entry, record the effects ... Journal entry is the process of recording the business transactions in the books of accounts for the ... Solved On July 1, 2015, ABC Co. issued 10-year, $4,574 ... - Chegg.com Question: On July 1, 2015, ABC Co. issued 10-year, $4,574 million maturity value, 3% coupon bonds when the market rate was 2% for a cash price of $4,994 million. Interest was payable semi-annually on December 31 and June 30. ABC also issued $3,527 million face value, 20-year, zero-coupon bonds on July 1, 2017, that mature June 30, 2037, for a ... Bonds Flashcards | Quizlet Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. Start studying the Bonds flashcards containing study terms like Which of the following statements are true about bonds: (more than one may be true) A. They are equity instruments B. They are debt instruments C. They are debt obligations with maturities longer than 7 (or 10) years D. Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1. Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: You must pay tax on interest annually even though you don't receive it until ...
Bonds in Finance Questions and Answers | Study.com Six year 9% bonds with a $450 000 par value are issued at a price of $479,435. Interest is paid semi-annually. The journal entry to record the issuance of this bond includes: A) A credit to cash fo... Mortgage-backed security - Wikipedia Just as this article describes a bond as a 30-year bond with 6% coupon rate, this article describes a pass-through MBS as a $3 billion pass-through with 6% pass-through rate, a 6.5% WAC, and 340-month WAM. The pass-through rate is different from the WAC; it is the rate that the investor would receive if he/she held this pass-through MBS, and the pass-through rate is almost always less than the ... Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - GitHub Pages Question: This $20,000 zero-coupon bond is issued for $17,800 so that a 6 percent annual interest rate will be earned. As shown in the above journal entry, the bond is initially recorded at this principal amount. Subsequently, two problems must be addressed by the accountant. First, the company will actually have to pay $20,000. Zero Coupon Bond Issued At Discount Amortization And Accounting Journal ... Accounting for a zero coupon bond issued at a discount (issue price less than face value) interest calculation and balance sheet recording, start with a cas...
Investment in Bonds | Journal Entry | Example - Accountinguide When the bond is redeemed by the issuer at the end of its maturity; Solution: On January 1, 2020. When the company ABC purchases the bond for $10,000 at its face value, it can make the investment in bonds journal entry on January 1, 2020, as below: Bond Retirement | Boundless Accounting | | Course Hero The journal entry to record the retirement of a bond: Debit Bonds Payable & Credit Cash. Learning Objectives ... Bonds can be classified to coupon bonds and zero coupon bonds. For coupon bonds, the bond issuer is supposed to pay both the par value of the bond and the last coupon payment at maturity. In case of a zero coupon bond, only the ... Zero Interest Bonds | Formula | Example | Journal Entry - Accountinguide Please prepare the journal entry during issuing and the annual interest expense. As the company issue bonds at zero interest rate, we need to calculate the selling price first. Selling price = $ 100/ (1+6%)^5 = $ 74.72 Company needs to sell bonds at $ 74.72 per bond. So the company will receive the cash of $ 74,270 for selling 1,000 bonds. Accounting for Bonds | Premium | Discount | Example ... Journal entry at the end of first year: On 31 Dec 202X, Company records debit interest expense of $ 7,588 ($ 94,846 * 8%), credit cash paid $ 6,000 and Discount bonds payable $ 1,588. Company record interest expense base on the market rate but pay to investor base on coupon rate, so the different will credit bond discount which will be zero at ...
Convertible zero-coupon bonds - journal entry Code: 3M originally sold $639 million in aggregate face amount of these "Convertible Notes" (zero-coupon bonds with maturity 30 years) on November 15, 2002, which are convertible into shares of 3M common stock. The gross proceeds from the offering, to be used for general corporate purposes, were $550 million ($540 million net of issuance costs).
Accounting Deep Discount Bonds - I GAAP & IFRS - CAclubindia A. Zero Coupon Bond (Deep Discount Bond) Zero-coupon bond (also called a discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond issued at a price lower than its face value, with the face value repaid at the time of maturity. It does not make periodic interest payments, or have so-called "coupons," hence the term zero-coupon bond.
Journal Entry for Bonds - Accounting Hub Therefore, the journal entry for semiannual interest payment is as follow: This interest payment will start from June 30, 2020, until December 31, 2039. At the maturity date, which is on December 31, 2039, the bonds will need to retire. Thus, ABC Co needs to repay back the principal of the bonds to the bondholders.
How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816)
Answered: YMMV Inc. issues a 6 year bond with a… | bartleby Texas Corporation has a level-coupon bond with a 9% coupon rate and is paid annually. The bond has 20 years to maturity and a face value of RM1,000; similar bonds currently yield 7%. By prior agreement, the company will skip the coupon interest payments in years 8, 9, and 10. These payments will be repaid, without interest, at maturity. Calculate the bond's current value.
Bond Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster bond: [verb] to lap (a building material, such as brick) for solidity of construction.
Accounting Zero Coupon Bonds Journal Entries Accounting Zero Coupon Bonds Journal Entries - ... Accounting Zero Coupon Bonds Journal Entries, Truck Lease Deals August 2020, Coupon For Celeb Boutique, Caress Body Wash Coupons 2020, About Faces Day Spa Coupons, Coupons Office Max 2019, Lee Valley Cyber Monday Deals 2019
Zero Coupon Bond (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) Zero-Coupon Bond (Also known as Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond) refers to those bonds which are issued at a discount to its par value and makes no periodic interest payment, unlike a normal coupon-bearing bond. In other words, its annual implied interest payment is included in its face value which is paid at the maturity of such bond.
Accounting For Bonds Payable - principlesofaccounting.com This topic is inherently confusing, and the journal entries are actually clarifying. Notice that the premium on bonds payable is carried in a separate account (unlike accounting for investments in bonds covered in a prior chapter, where the premium was simply included with the Investment in Bonds account).
Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - XPLAIND.com A zero-coupon bond is a bond which does not pay any periodic interest but whose total return results from the difference between its issuance price and maturity value. For example, if Company Z issues 1 million bonds of $1000 face value bonds due to maturity in 5 years but which do not pay any interest, it is a zero-coupon bond.
PubMed Moved Permanently. The document has moved here.
Original Issue Discount (OID) - What Is It? Example and ... - CFAJournal See also Interest on Debentures: Accounting and Journal Entries. The bond issuers offer a higher discount on zero-coupon bonds. Zero-coupon bonds do not pay regular interest payments to the investors instead the investors look to realize profits with capital gains. If the bonds do not sell the investor's only return with a zero-coupon bond ...
Answered: YMMV Inc. issues a 6 year bond with a… | bartleby Texas Corporation has a level-coupon bond with a 9% coupon rate and is paid annually. The bond has 20 years to maturity and a face value of RM1,000; similar bonds currently yield 7%. By prior agreement, the company will skip the coupon interest payments in years 8, 9, and 10. These payments will be repaid, without interest, at maturity.
Bonds Flashcards - Quizlet Which of the following are true about Zero coupon bonds (more than one may be true): A. A zero coupon bond pays interest each period B. The market value of a zero coupon bond is just the discounted value of the final par value payment. C. Zero coupon bonds are issued at par value. D. Zero coupon bonds are issued at below par value
Accounting for Bonds | Premium - Example - Accountinguide Journal entry at the end of first year: On 31 Dec 202X, Company records debit interest expense of $ 7,588 ($ 94,846 * 8%), credit cash paid $ 6,000 and Discount bonds payable $ 1,588. Company record interest expense base on the market rate but pay to investor base on coupon rate, so the different will credit bond discount which will be zero at the end of bond term.










Post a Comment for "38 zero coupon bond journal entry"